High Dynamic Range Video Coding
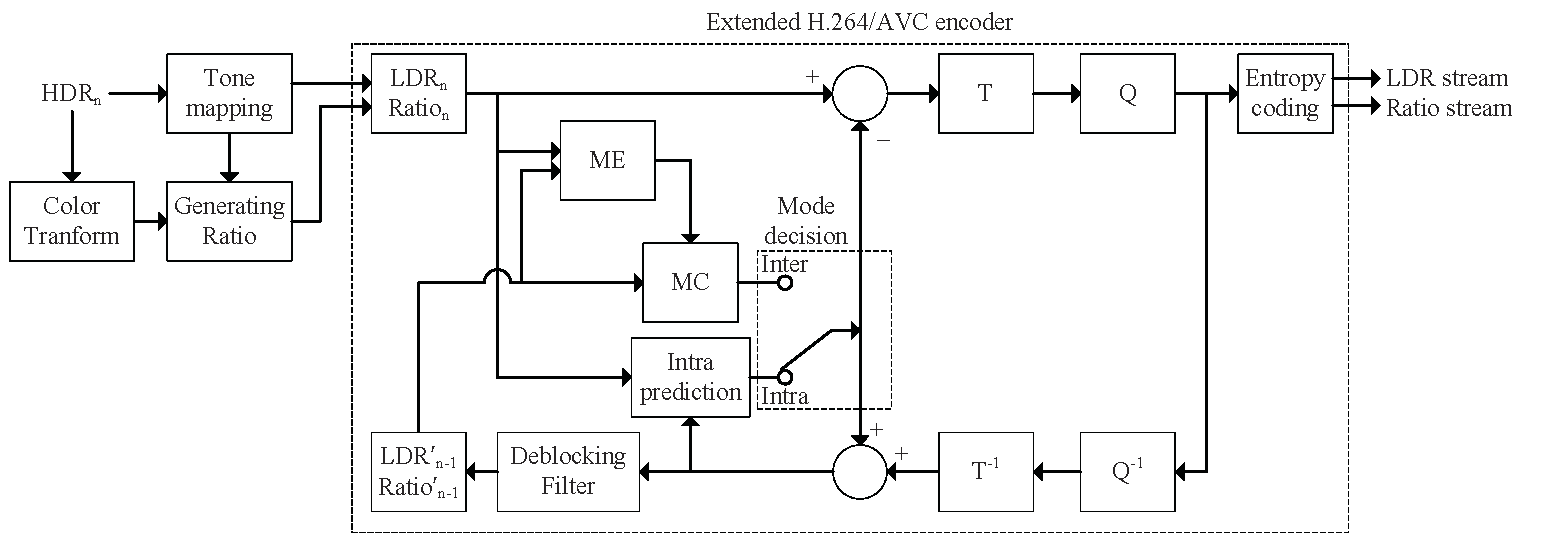 |
The block diagram of the proposed HDR video encoder. An input HDR frame is tone-mapped and decomposed into an LDR frame and a ratio frame. Then, the LDR and ratio frames are encoded with a modified H.264 encoder to produce two streams: an LDR stream as a base layer and a ratio stream as an enhancement layer. ME stands for motion estimation, MC motion-compensated prediction, T transform, and Q quantizer.
Abstract
An efficient algorithm to compress high dynamic range (HDR) videos into layered bitstreams is proposed in this work. First, we separate an HDR video sequence into a tone-mapped low dynamic range (LDR) sequence and a ratio sequence, which represents ratios between HDR and LDR pixel values. Then, we encode the LDR and ratio sequences to maximize the rate-distortion (R-D) performance by extending the standard H.264/AVC codec. Specifically, we estimate the distortion of the HDR sequence from those of the LDR sequence and the ratio sequence, and then allocate a limited bit budget to the LDR sequence and the ratio sequence efficiently to maximize the qualities of both LDR and HDR sequences. Conventional LDR devices use only the LDR stream, whereas HDR devices reconstruct the HDR video from the LDR and ratio streams. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm provides significantly better R-D performance than conventional HDR video coding techniques.
Experimental Results
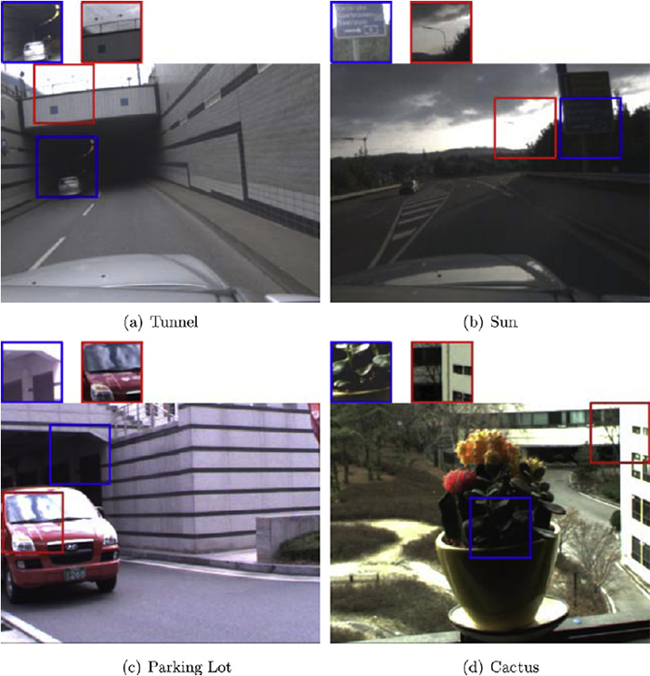 |
Examples of reconstructed HDR frames. The pixel values in each region, marked by a blue or red rectangle, are linearly scaled to a displayable range and shown separately.
Publications
Chul Lee and Chang-Su Kim, “Rate-distortion optimized compression of high dynamic range videos,” in Proc. European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Lausanne, Switzerland, Aug. 2008.
Chul Lee and Chang-Su Kim, “Rate-distortion optimized layered coding of high dynamic range videos,” Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 908-923, Aug. 2012.
Code
will be available soon